Dropshipping has become popular in recent years. It has low entry barriers and does not require inventory. This makes it a great option for new sellers.
However, expanding your business into international markets often brings complex tax policies that can be a headache. Without understanding these in advance, your profit margins may suffer, and you could even face compliance risks.
Today, we will talk about tax issues for dropshipping sellers. We will focus on important markets like the U.S., EU, Australia, and Canada.
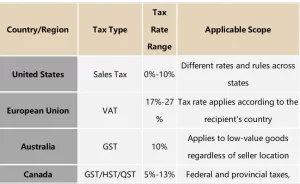
United States: Sales Tax Varies by State

In the U.S., sales tax can be quite complicated since each state has its own regulations. In simple terms, if your dropshipping business creates an “economic nexus” in a state, you must collect sales tax. This happens when you meet a specific sales threshold in that state.
Tax rates can be very different. For example, California has an average sales tax of 7.25%. In contrast, Oregon has no sales tax at all.
It is important for dropshipping sellers to know where they have an economic nexus. They should also check the tax rates in those states.
Sales tax rates in the U.S. can vary a lot. Some rates are close to 10%. However, some states do not collect sales tax at all. For dropshipping sellers, setting the right prices according to state tax rates is essential to ensure profitability.
European Union: Uniform Rules for Value-Added Tax (VAT)

Compared to the U.S., the EU has a more unified tax policy. All sellers who sell goods within the EU must pay Value-Added Tax (VAT), regardless of their location. However, each country’s VAT rate varies, such as 19% in Germany and 25% in Sweden. This means that when selling to EU countries, you must collect and remit VAT according to the destination country’s rate.
For example, if you sell a product in France priced at €100, the 20% VAT will add €20 to the total price. Simply put, when selling within the EU, you need to consider each country’s VAT rate to price products accurately.
Looking at the data, VAT rates in the EU generally range between 17% and 27%. Luxembourg has the lowest rate at 17%, while Hungary has the highest at 27%.
Australia: Key Points for Dropshipping Sellers on Tax Rules

Australia has strict tax policies for imported goods. All imported items, regardless of value, must include a Goods and Services Tax (GST). For dropshipping sellers, this means that any item sent to Australia requires you to collect a 10% GST. This rule applies to goods valued under AUD 1,000, regardless of your location.
For example, if you sell a product to an Australian customer for AUD 800, you add 10% GST. This means an extra AUD 80 in taxes. This shows that dropshipping sellers need to consider GST when setting prices. This helps them stay competitive and keep their profit margins.
Canada: Dual Challenge of Provincial and Federal Taxes

Canada’s tax system is relatively complex, requiring dropshipping sellers to understand both federal and provincial tax policies. At the federal level, there is a Goods and Services Tax (GST) of 5%.
Some provinces may add extra taxes. For example, Quebec has the Quebec Sales Tax (QST) and the Harmonized Sales Tax (HST). Tax rates vary by province, with Ontario’s HST at 13%, while Alberta only collects GST at 5%.
For dropshipping sellers, this means you must accurately calculate taxes based on the customer’s location. When selling to different provinces, understanding the applicable tax rates is essential for compliant operations. Additionally, incorporating taxes into your pricing strategy helps avoid profit loss due to tax miscalculations. Mastering Canada’s tax rules is a key step for successfully expanding into the local market.
When doing dropshipping globally, tax policies vary widely. Below is an overview of the tax regulations in major markets:
Tax Challenges in Cross-Border Dropshipping: How to Effectively Manage Them?

In cross-border dropshipping operations, tax issues are often one of the most challenging aspects for sellers. Different countries and regions have their own tax rules. Understanding and managing these rules can be challenging for many sellers.
To stay competitive in the global market, you must handle tax issues properly. This will help ensure your business’s long-term stability. Today, we will discuss how to handle tax challenges in dropshipping. This will help you manage the complexities of cross-border e-commerce easily.
Understand the Tax Policies of Your Target Markets
Different countries and regions have their own tax regulations and requirements. Some countries impose Value-Added Tax (VAT) on imported goods, while others have Goods and Services Tax (GST) or Sales Tax. As a dropshipping seller, start by thoroughly understanding the tax policies of your target markets. For example:
United States: Each state has different sales tax rules. Some states do not collect sales tax, while others have rates as high as 10%.
European Union: VAT is uniformly required, but rates vary between 17% and 27% depending on the country.
Australia charges a 10% GST on imported goods, regardless of the seller’s location.
Knowing these rules helps you make better pricing strategies for different countries. This can help you avoid tax problems that might affect your profits.
Adjust Pricing Strategies Flexibly
Dropshipping sellers can change their pricing strategies based on tax rules in different markets. If a market has high tax rates, you might include taxes in the price. You could also raise the selling price a little to stay competitive.
For example, in Canada, tax rates vary significantly by province. Ontario’s HST rate is 13%, while Alberta only has a 5% GST. Sellers can create flexible pricing strategies based on the tax rules of each province. This helps them stay compliant and increase profits.

Use Professional Tax Services or Software
Dealing with the complex tax systems of multiple countries and regions manually is time-consuming and error-prone. Fortunately, many specialized tax services and software can help dropshipping sellers overcome these challenges. Tools like Avalara and TaxJar automate tax calculation and filing for different regions, ensuring your business remains compliant. These tools not only reduce tedious workloads but also help you avoid costly penalties from tax errors.
Plan Taxes in Advance
Tax planning is crucial for dropshipping businesses. When entering new markets, a clear tax strategy can help you avoid compliance risks later on. For instance, some countries require registration and tax collection only after reaching certain sales thresholds or order volumes. Understanding these thresholds allows you to plan your market expansion sequence and optimize your cost structure effectively.
Consult Professional Tax Advisors
If your budget allows, consulting a professional international tax advisor is highly recommended. Tax advisors can provide personalized advice based on your business model, target markets, and specific needs. A professional advisor helps you understand tax rules. They also offer the best tax solutions to lower costs and avoid problems.
Conclusion
As dropshipping businesses grow around the world, tax rules in different countries have become a significant challenge for sellers. Understanding and addressing these tax issues helps avoid compliance risks. It also optimizes costs and increases profit margins.
Sellers can simplify cross-border tax processes and lower their tax burden. They can do this by understanding tax policies in target markets. They should also adjust pricing strategies as needed. Using professional tax tools or advisors can help them succeed.


 8 min read
8 min read






